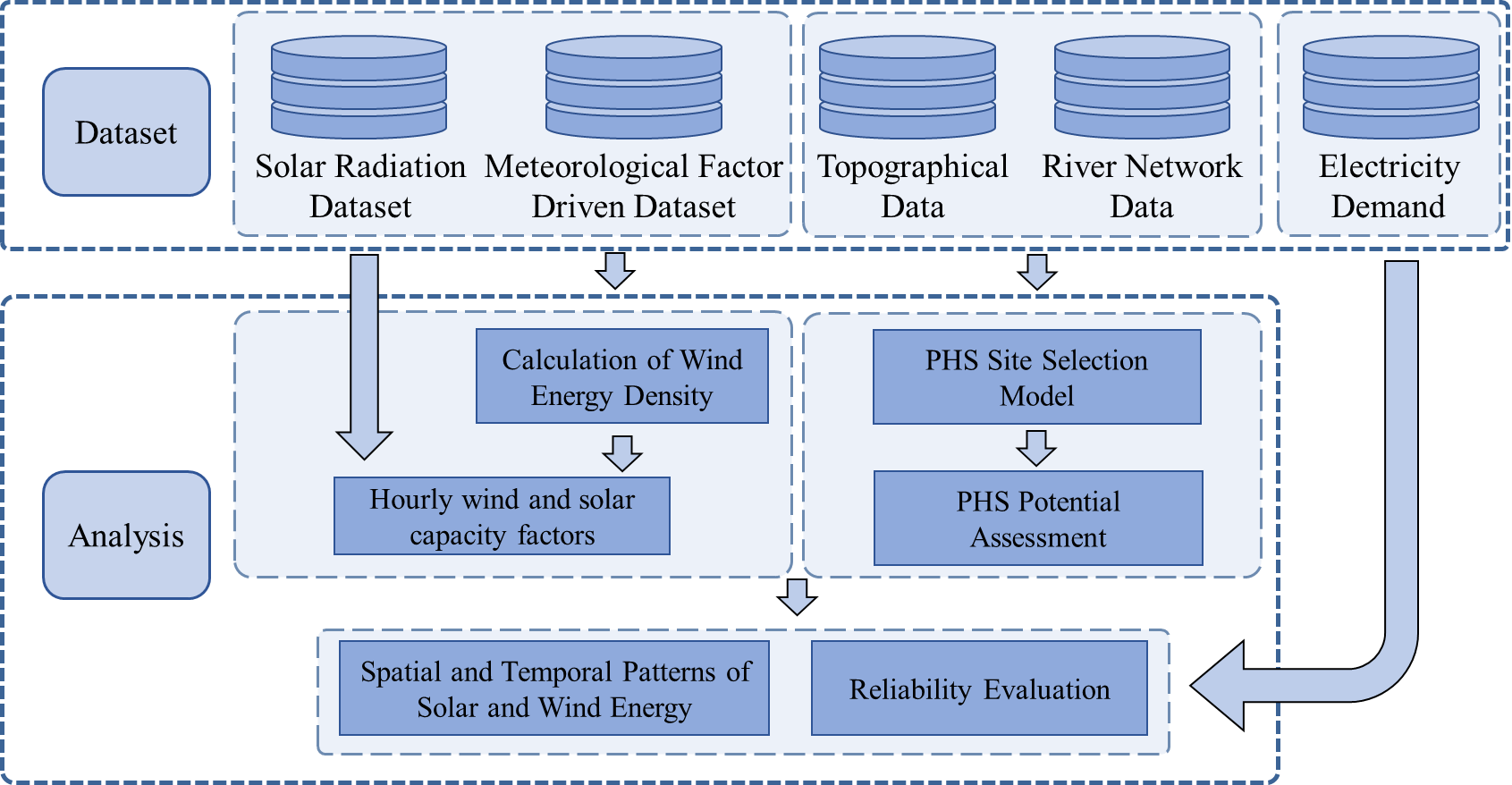
The group has made research progress in the study of assessing the potential and complementarity of wind-water multi-energy sources:

Wind and solar energy is one of the most important clean energy sources globally, which suffers from severe intermittency and supply-demand imbalance in time and space due to weather variability. Pumped storage, as an important energy storage device, has great potential to improve the intermittency and volatility of wind and solar energy, but no study has yet evaluated the potential of pumped storage in regulating wind and solar power generation across China. To address this issue, the team's undergraduate student, Xinyi Fan, published her research results entitled “Assessment of Potential Complementarity of Pumped Hydropower Storage to Solar and Wind Energy” in January 2025 in Transactions in GIS.
The study first evaluates China's energy reliability under various scenarios by calculating the ratio between energy demand and supply in the context of different wind and solar energy combinations. Next, an algorithmic model is designed to estimate pumped storage site location and storage capacity for the whole country. Finally, the energy reliability of the two scenarios with and without pumped storage is compared.
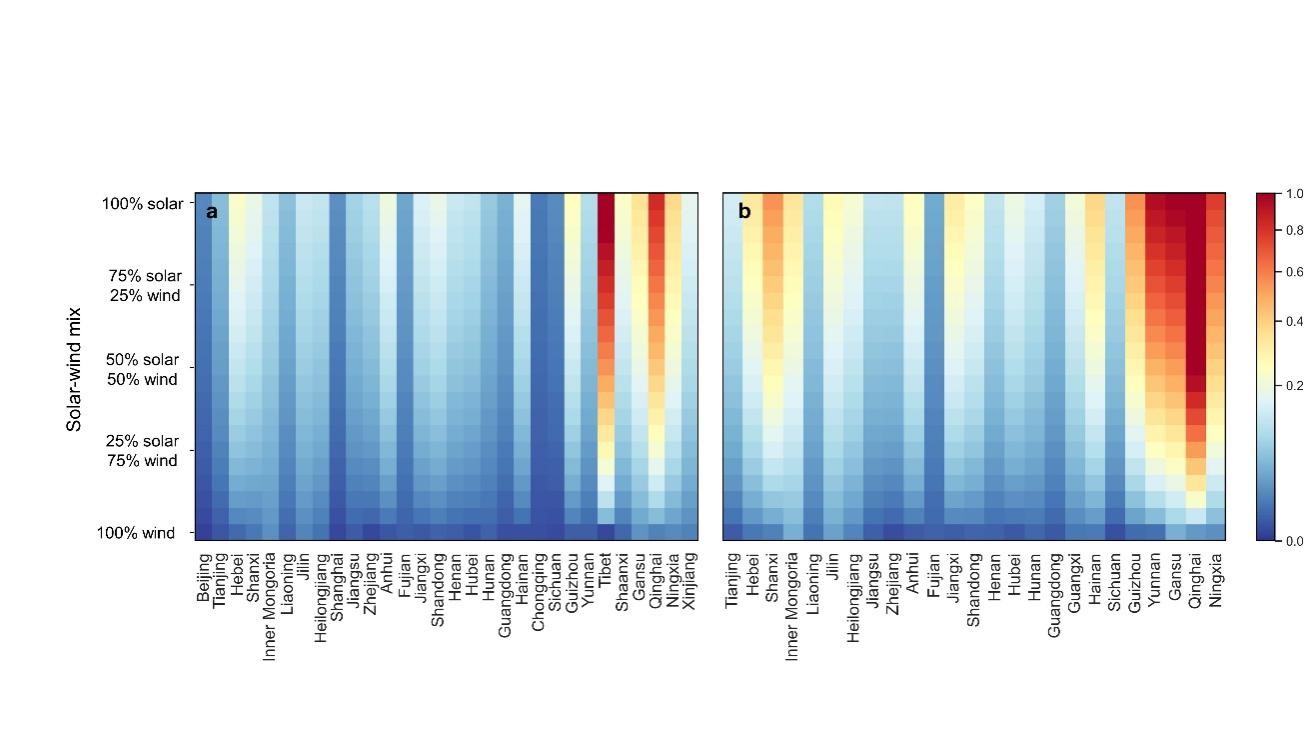
The results show that in the absence of storage and inter-provincial energy transmission capacity, the reliability of electricity supplied by a combination of solar and wind energy remains low in most provinces, typically not exceeding 30 percent. Even though reliability may improve in some provinces in 2025 as renewable energy capacity increases, it is still projected to be below 50 percent in most provinces.
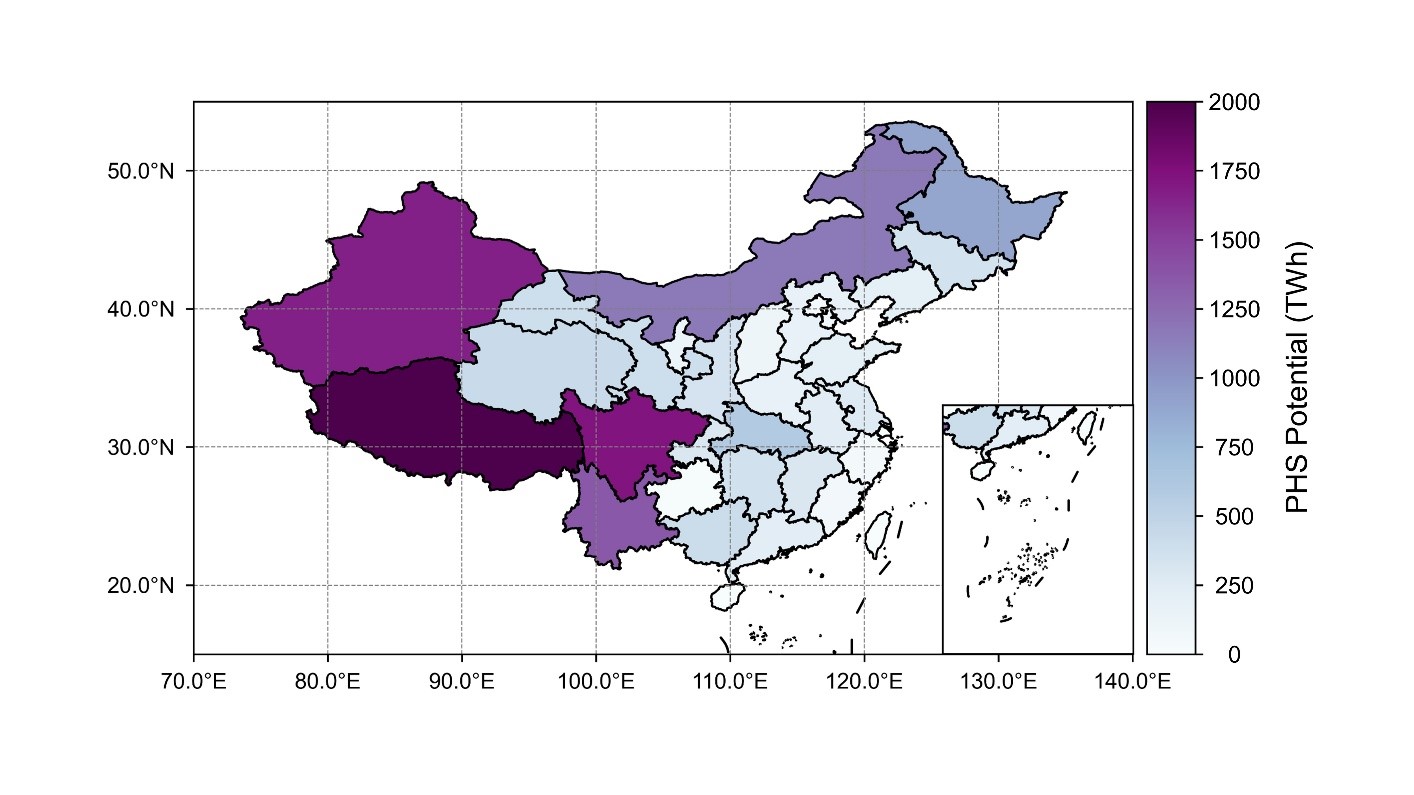
Before assessing the reliability potential of combined solar and wind power supply in the case of energy storage, we first assessed the potential of pumped storage in all provinces of China based on a siting model. In comparison with the actual scale of current pumped storage development, it is concluded that there is still considerable potential for pumped storage power plant development in China.
Under pumped storage storage conditions, the reliability of both wind and solar energy improves in most provinces, with significant reliability improvements in Southwest, Northwest, and Northeast China, and relatively small improvements in Southeast and North China. This is in contradiction with the spatial distribution of electricity demand, and therefore, inter-regional power transmission should be considered to improve the stability of power supply in high-demand areas.
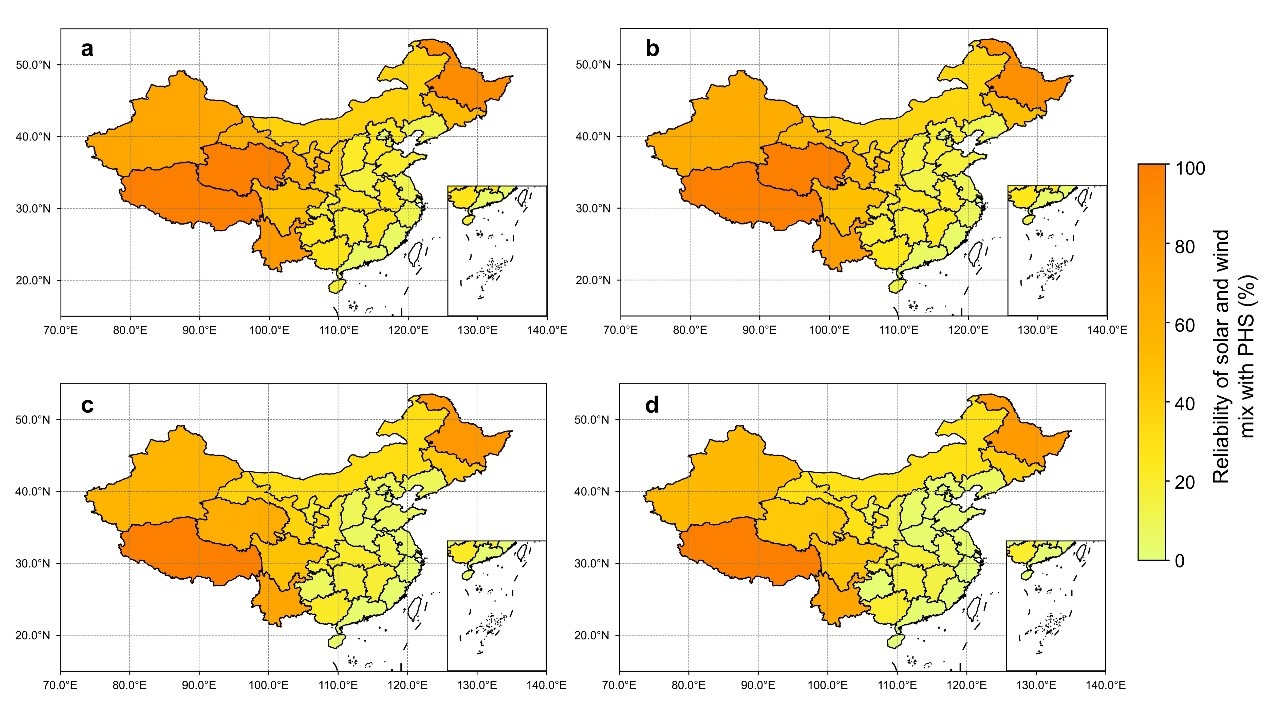
This study emphasizes the important role of pumped storage in improving the stability and reliability of renewable energy generation, which is important for guiding the layout and construction of future renewable energy and energy storage infrastructure.
First author: Xinyi Fan
Corresponding author: Assoc. Prof. Jun Zhang
Other authors: Yuqi Song, Prof. Julian Hunt, Prof. Qiang Dai
Link to the paper: https://doi.org/10.1111/tgis.70001